The Sun
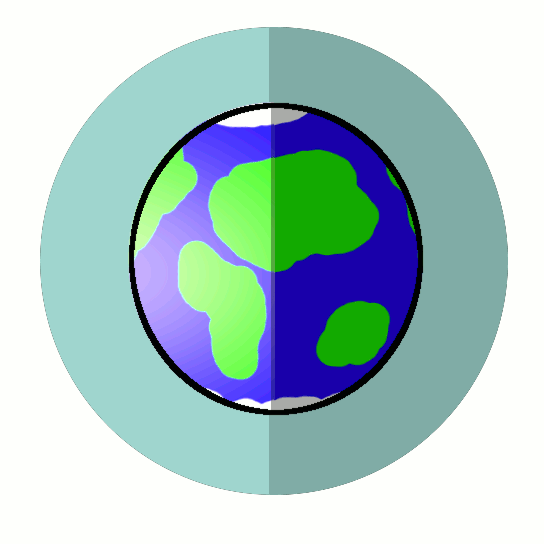
The Sun makes all weather on the Earth. The Sun heats the Earth's ground, oceans, and air. Only the side of the Earth that faces the sun is heated by the Sun. The Earth rotates around its axis like a spinning top.
Seasons
The Earth also revolves around the sun causing the seasons. Winter, Summer, Autumn, and Spring have different temperatures. This is because the Earth is tilted on its axis of rotation.
The seasons are Autumn, Winter, Spring, and then Summer.
In Autumn the leaves change from green to yellow or red to keep the ground warm and protect the roots of trees from cold. Trees, animals, and people start preparing for the cold winter.
In ancient times, crops were harvested by the village folk in Autumn - and the season was referred to as Harvest.
In North America, Autumn is also called Fall - because of the falling leaves.
The Oceans
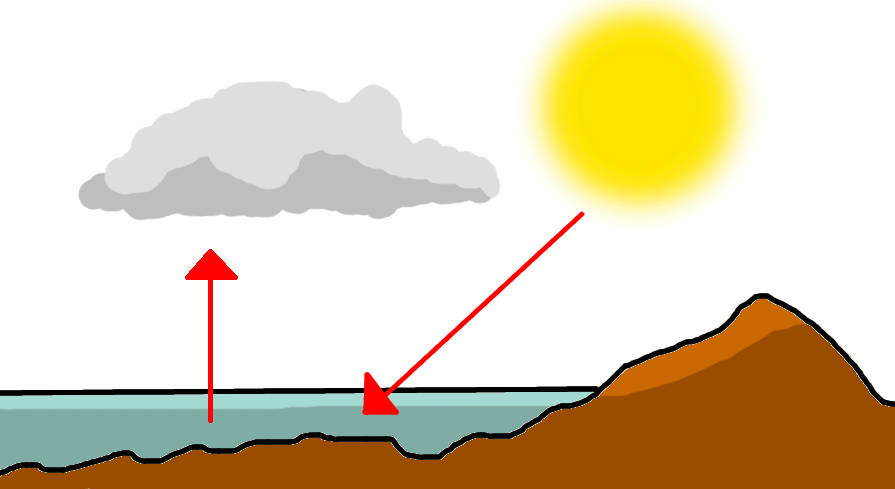
The Oceans are heated by the Sun. Just like boiling a kettle the Sun heats the water in the oceans and some of this water evaporates.
Clouds
The evaporated water rises into the atmosphere forming clouds. There are different types of clouds, such as:
- Cirrus - wispy clouds
- Cumulonimbus - big clouds with lots of rain
- Stratus - very high thin and flat clouds
Wind and Rain
The wind blows the clouds over the land and when conditions are just right the clouds make rain droplets which then fall to the earth. This is how rain is made.
Rain is made when tiny droplets of water inside clouds collide to form larger drops of water that eventually become heavy and fall to Earth.
There are different types of rain including:
- Drizzle - light rain
- Normal rain
- Freezing rain - rain that freezes when it contacts an object
When clouds bump into mountains the water droplets in the clouds are forced together to form rain.
Humidity
The air or atmosphere consists of many atoms and molecules, including:
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Water
- Trace Gases (methane, neon, helium and more)
Humidity is a measure of how much water there is in the air.
"100% relative humidity" means that the air is completely saturated with water.
When the sun heats water, water molecules escape from the surface of the water through evaporation and into the air.
Warm air rises.
Warmer water molecules are more energetic and stay in the air longer than cool water molecules. Warmer air is more likely to have more moisture.
When warm air rises and cools, the water becomes less energetic and rain droplets form. This is how rain is made.
Pressure, Dew Point, and Precipitation
Pressure
A drop in atmospheric pressure is often associated with cloudy or rainy weather. Conversely, high pressure is usually associated with fair weather. Variations in pressure lead to the development of winds, which in turn influence our daily weather.
Dew Point
The dew point temperature is the temperature to which the air must be cooled to reach saturation (assuming air pressure remains the same). The dew point is a direct measure of the amount of moisture present in the air, and directly affects how you feel... or in other words... measures the amount of humidity in the air. Remember, the temperature never drops below its dew point but can drop to it. Generally, we start to feel some discomfort when the dew point gets to or just above 60 degrees Chance of
Precipitation
Precipitation is any kind of water that falls from the sky as part of the weather. This includes snow, rain, sleet, freezing rain, hail, and virga.
What types of clouds do you see in this photo?
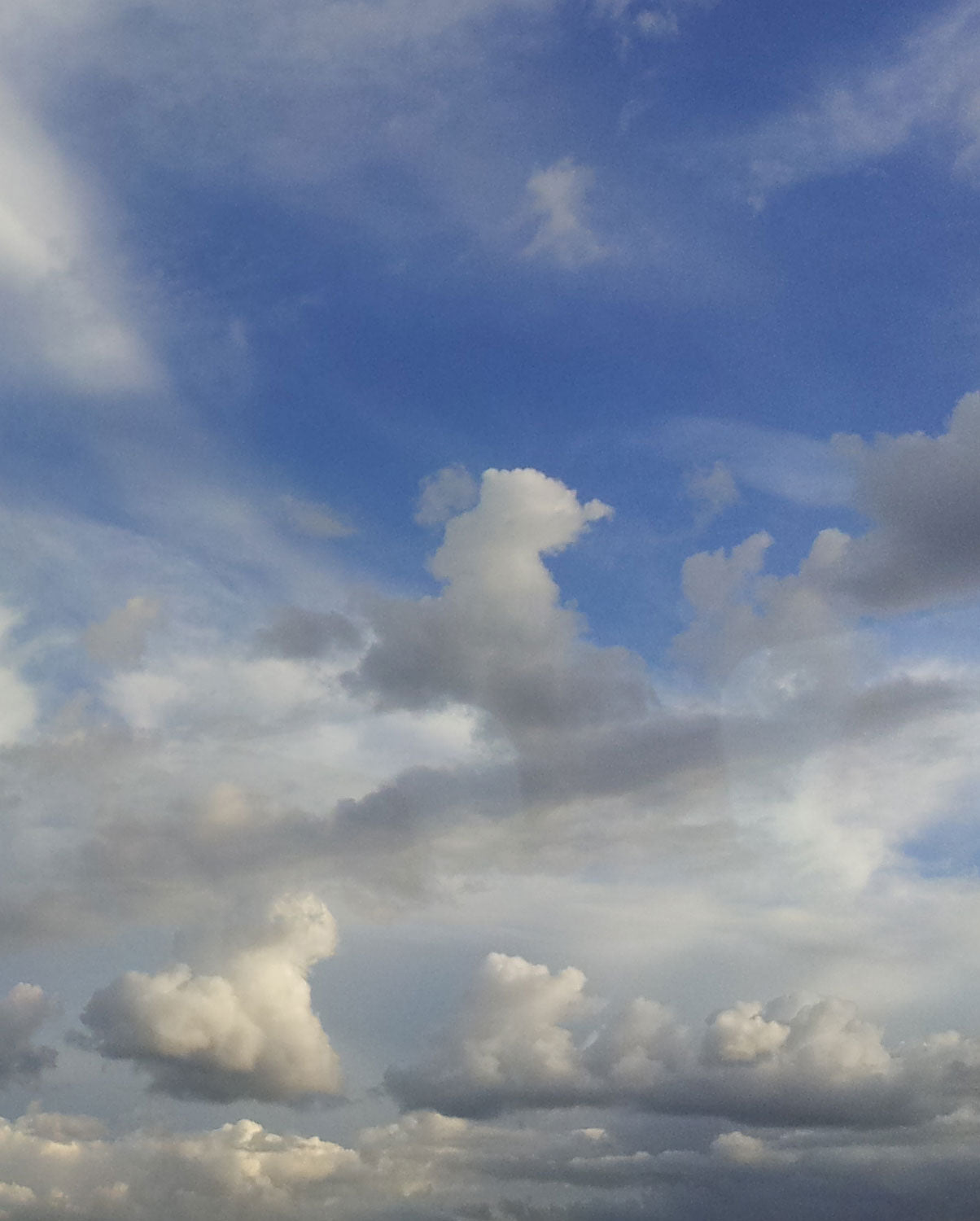

Clouds over London, England
Fun Weather Activities
Please register before downloading.
